THE UNIVERSITY OF THE STATE OF NEW YORK• THE STATE EDUCATION DEPARTMENT• ALBANY, NY 12234
Reference Tables for Physical Setting/CHEMISTRY
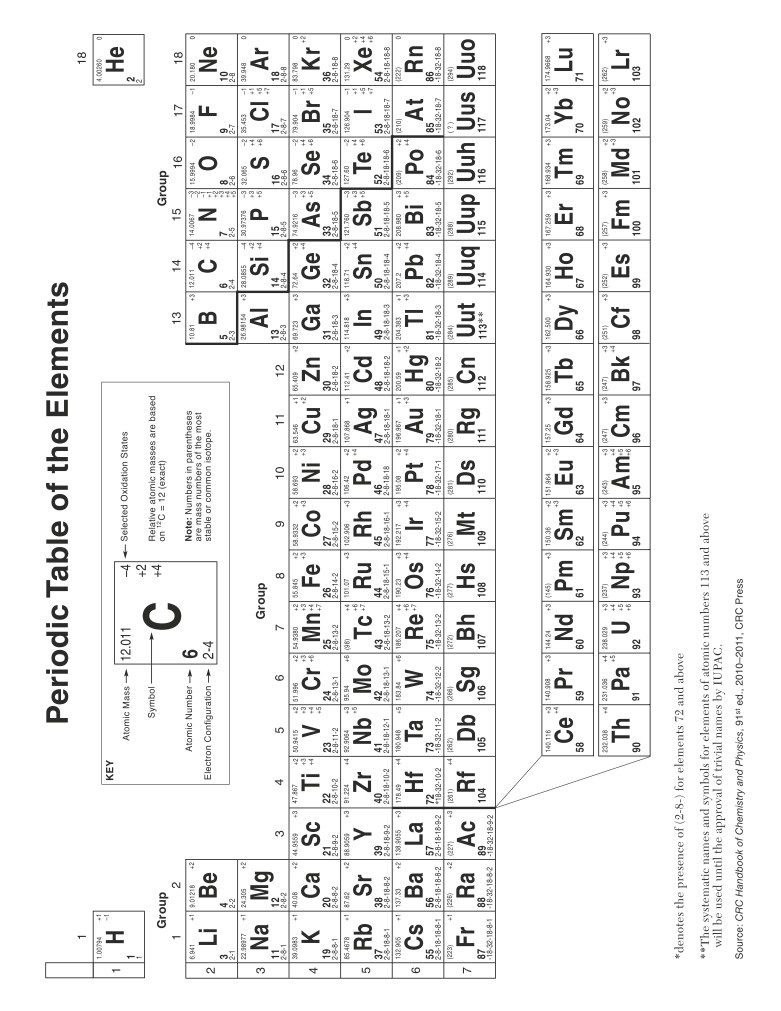
C
2011 Edition
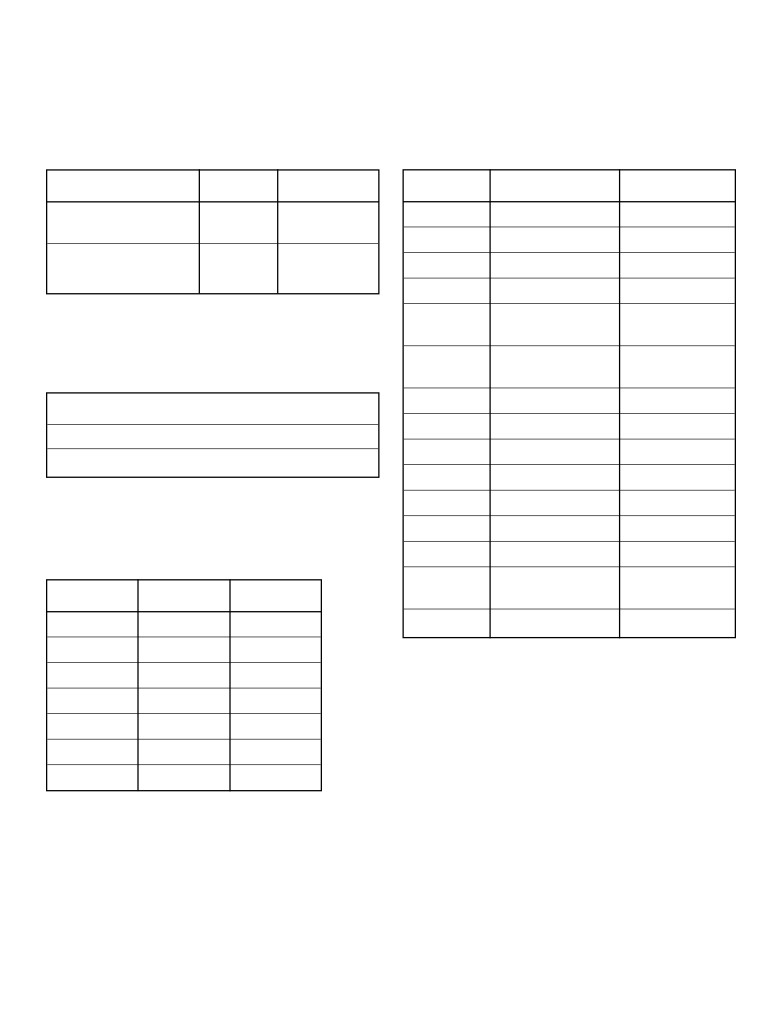
Table A
Table D
Standard Temperature and Pressure
Selected Units
Name
Value
Unit
Symbol
Name
Quantity
Standard Pressure
101.3 kPa
kilopascal
m
meter
length
1 atm
atmosphere
g
gram
mass
Standard Temperature
273 K
kelvin
Pa
pascal
pressure
0°C
degree Celsius
K
kelvin
temperature
amount of
mol
mole
substance
Table B
energy, work,
J
joule
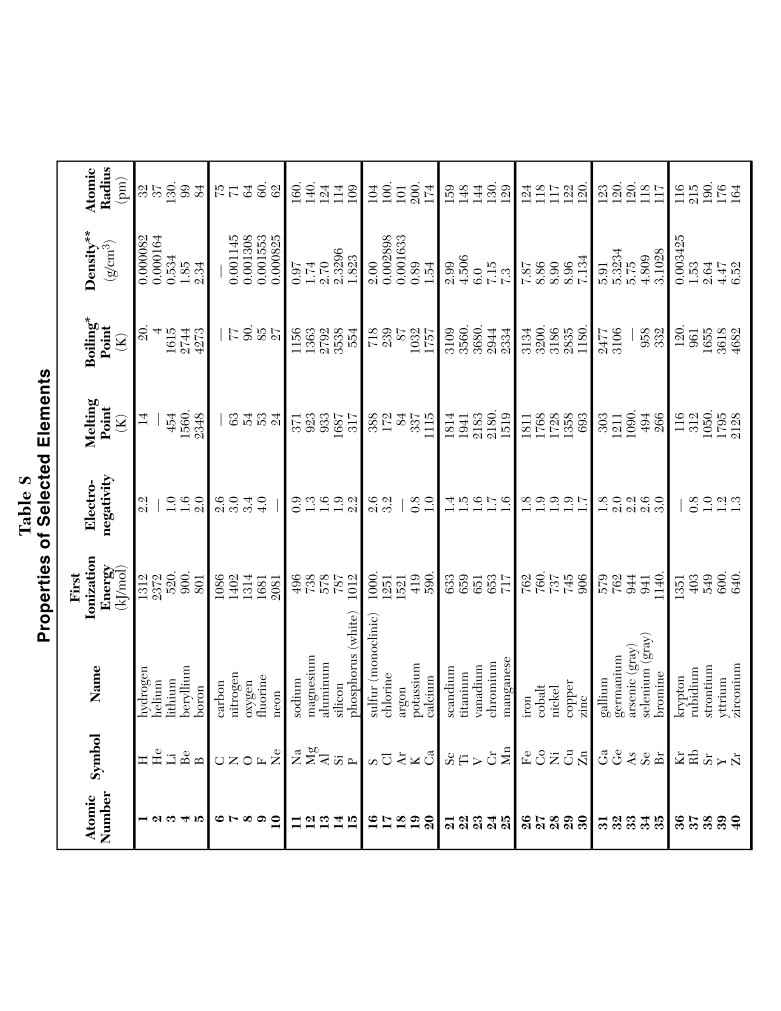
Physical Constants for Water
quantity of heat
s
second
time
Heat of Fusion
334 J/g
min
minute
time
Heat of Vaporization
2260 J/g
h
hour
time
Specific Heat Capacity of H2O( )
4.18 J/g•K
d
day
time
y
year
time
L
liter
volume
Table C
ppm
parts per million
concentration
Selected Prefixes
solution
M
molarity
concentration
Factor
Prefix
Symbol
103
kilo-
k
u
atomic mass unit
atomic mass
10-1
deci-
d
10-2
centi-
c
10-3
milli-
m
10-6
micro-
μ
10-9
nano-
n
10-12
pico-
p
Reference Tables for Physical Setting/Chemistry - 2011 Edition
1
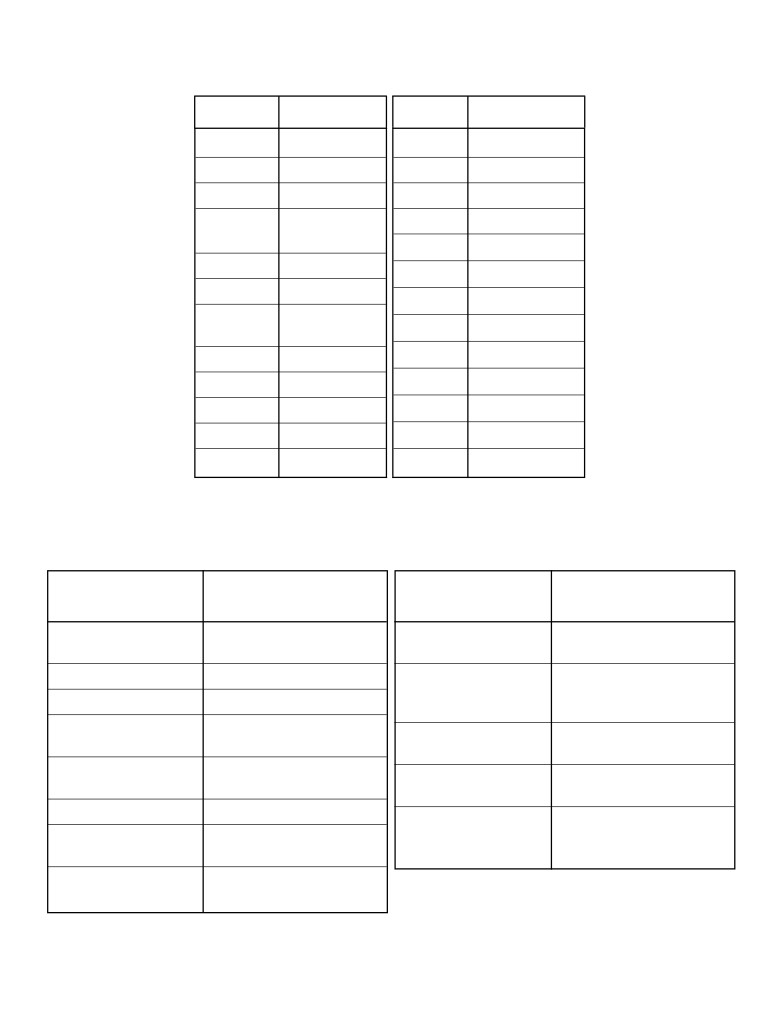
Table E
Selected Polyatomic Ions
Formula
Name
Formula
Name
H3O+
hydronium
Cr O42-
chromate
Hg22+
mercury(I)
Cr2O72-
dichromate
NH4+
ammonium
MnO4-
permanganate
C2H3O2-
NO2-
nitrite
acetate
CH3COO-}
NO3-
nitrate
CN-
cyanide
O22-
peroxide
CO32-
carbonate
OH-
hydroxide
HCO3-
hydrogen
PO43-
phosphate
carbonate
SCN-
thiocyanate
C2O42-
oxalate
ClO-
hypochlorite
SO32-
sulfite
ClO2-
chlorite
SO42-
sulfate
ClO3-
chlorate
HSO4-
hydrogen sulfate
ClO4-
perchlorate
S2O32-
thiosulfate
Table F
Solubility Guidelines for Aqueous Solutions
Ions That Form
Ions That Form
Soluble Compounds
Exceptions
Insoluble Compounds*
Exceptions
Group 1 ions
carbonate (CO32-)
when combined with Group 1
(Li+, Na+, etc.)
ions or ammonium (NH4+)
ammonium (NH4+)
chromate (CrO42-)
when combined with Group 1
ions, Ca2+, Mg2+, or
nitrate (NO3-)
ammonium (NH4+)
acetate (C2H3O2- or
phosphate (PO43-)
when combined with Group 1
CH3COO-)
ions or ammonium (NH4+)
hydrogen carbonate
sulfide (S2-)
when combined with Group 1
(HCO3-)
ions or ammonium (NH4+)
chlorate (ClO3-)
hydroxide (OH-)
when combined with Group 1
halides (Cl-, Br-, I-)
when combined with
ions, Ca2+, Ba2+, Sr2+, or
2+
Ag+, Pb2+, or Hg2
ammonium (NH4+)
sulfates (SO42-)
when combined with Ag+,
*compounds having very low solubility in H2O
Ca2+, Sr2+, Ba2+, or Pb2+
Reference Tables for Physical Setting/Chemistry - 2011 Edition
2
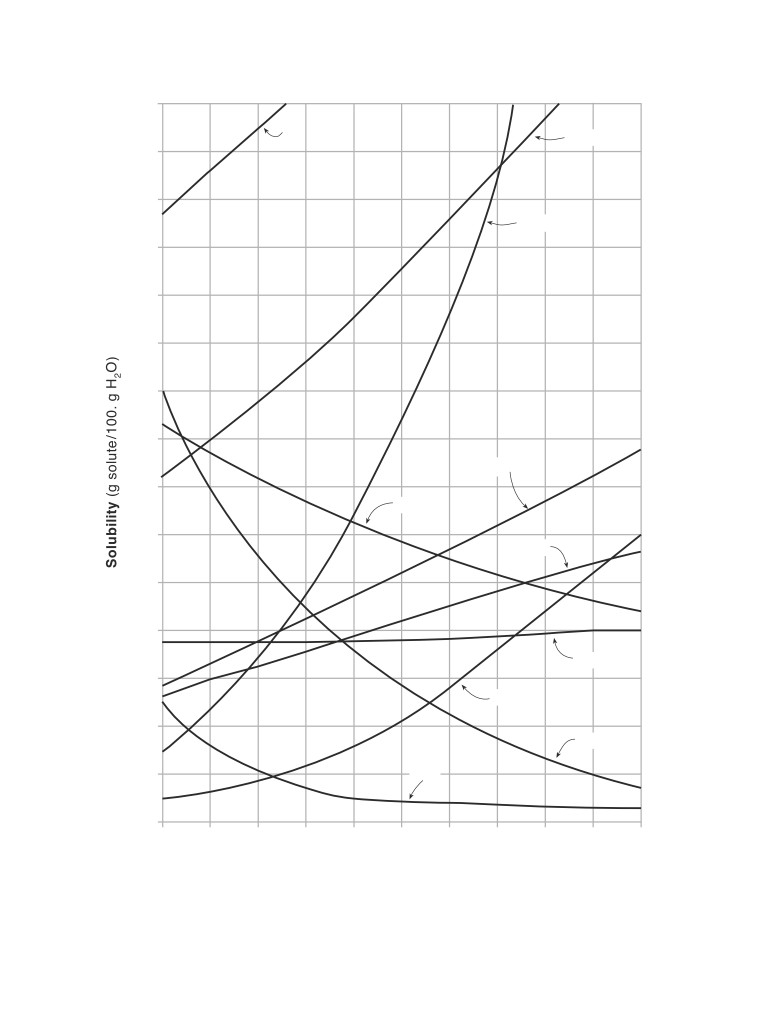
Table G
Solubility Curves at Standard Pressure
150.
KI
NaNO
3
140.
130.
KNO3
120.
110.
100.
90.
80.
NH4Cl
70.
HCl
60.
KCl
50.
40.
NaCl
30.
KClO3
20.
NH3
SO2
10.
0
0
10.
20.
30.
40.
50.
60.
70.
80.
90.
100.
Temperature (°C)
Reference Tables for Physical Setting/Chemistry - 2011 Edition
3
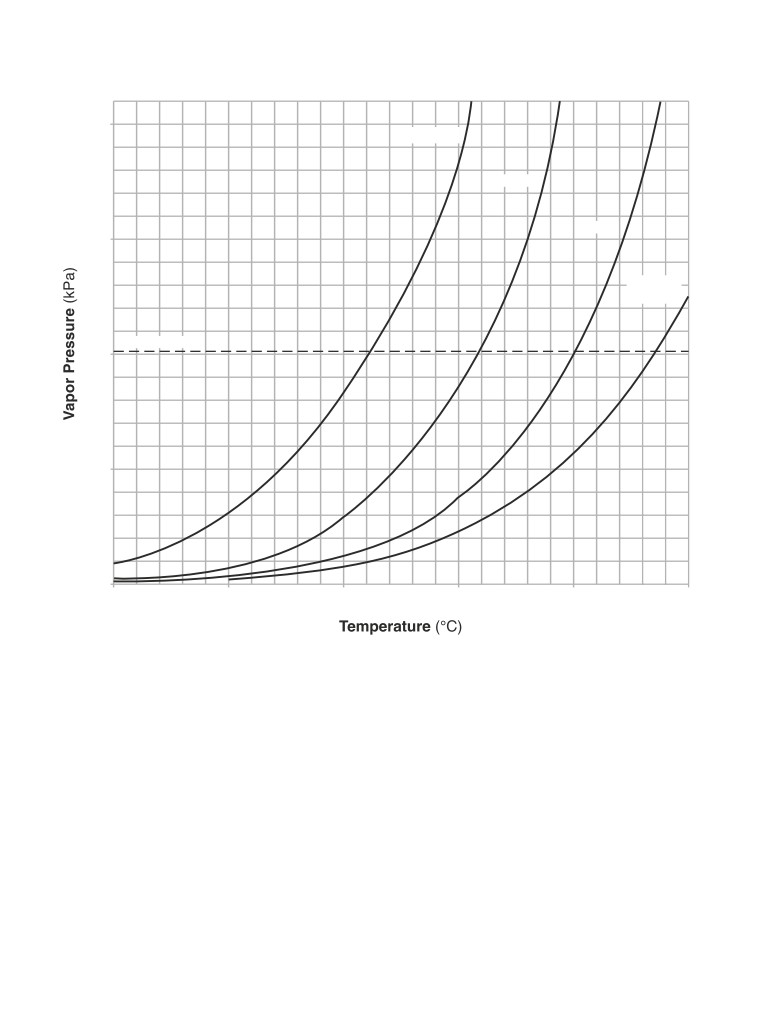
Table H
Vapor Pressure of Four Liquids
200.
propanone
ethanol
water
150.
ethanoic
acid
101.3 kPa
100.
50.
0
0
25
50.
75
100.
125
Reference Tables for Physical Setting/Chemistry - 2011 Edition
4
Table I
Table J
Heats of Reaction at 101.3 kPa and 298 K
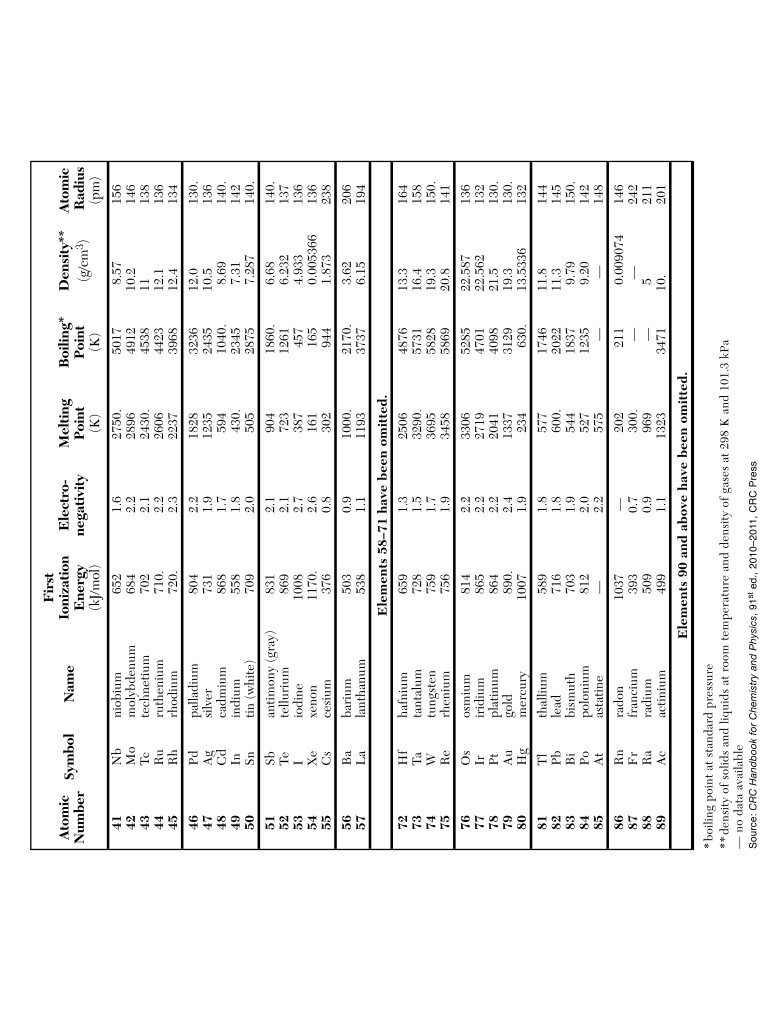
Activity Series**
Reaction
ΔH (kJ)*
Most
Metals
Nonmetals
Most
Active
Active
CH4(g) + 2O2(g)
CO2(g) + 2H2O( )
-890.4
Li
F2
C3H8(g) + 5O2(g)
3CO2(g) + 4H2O( )
-2219.2
Rb
Cl2
2C8H18( ) + 25O2(g)
16CO2(g) + 18H2O( )
-10943
K
Br2
2CH3OH( ) + 3O2(g)
2CO2(g) + 4H2O( )
-1452
Cs
I
2
C2H5OH( ) + 3O2(g)
2CO2(g) + 3H2O( )
-1367
Ba
C6H12O6(s) + 6O2(g)
6CO2(g) + 6H
O( )
-2804
Sr
2
2CO(g) + O2(g)
2CO2(g)
-566.0
Ca
C(s) + O2(g)
CO2(g)
-393.5
Na
4Al(s) + 3O2(g)
2Al2O3(s)
-3351
Mg
N2(g) + O2(g)
2NO(g)
+182.6
Al
N2(g) + 2O2(g)
2NO2(g)
+66.4
Ti
2H2(g) + O2(g)
2H2O(g)
-483.6
Mn
2H2(g) + O2(g)
2H2O( )
-571.6
Zn
N2(g) + 3H2(g)
2NH3(g)
-91.8
Cr
2C(s) + 3H2(g)
C2H6(g)
-84.0
Fe
2C(s) + 2H2(g)
C2H4(g)
+52.4
Co
2C(s) + H2(g)
C2H2(g)
+227.4
Ni
H2(g) + I2(g)
2HI(g)
+53.0
Sn
KNO3(s) H2O K+(aq) + NO
-(aq)
+34.89
Pb
3
NaOH(s) H2O Na+(aq) + OH-(aq)
-44.51
H2
NH4Cl(s) H2O NH
+(aq) + Cl-(aq)
+14.78
Cu
4
NH
+25.69
Ag
4NO3(s) H2O NH4+(aq) + NO3-(aq)
NaCl(s) H2O Na+(aq) + Cl-(aq)
+3.88
Au
Least
Least
Active
Active
LiBr(s) H2O Li+(aq) + Br-(aq)
-48.83
H+(aq) + OH-(aq)
H2O( )
-55.8
**Activity Series is based on the hydrogen
standard. H2 is not a metal.
* The ΔH values are based on molar quantities represented in the equations.
A minus sign indicates an exothermic reaction.
Reference Tables for Physical Setting/Chemistry - 2011 Edition
5
Table K
Table N
Common Acids
Selected Radioisotopes
Formula
Name
Nuclide
Half-Life
Decay
Nuclide
Mode
Name
HCl(aq)
hydrochloric acid
198Au
2.695 d
β-
gold-198
HNO2(aq)
nitrous acid
14C
5715 y
β-
carbon-14
HNO3(aq)
nitric acid
37Ca
182 ms
β+
calcium-37
H2SO3(aq)
sulfurous acid
60Co
5.271 y
β-
cobalt-60
H2SO4(aq)
sulfuric acid
137Cs
30.2 y
β-
cesium-137
H3PO4(aq)
phosphoric acid
53Fe
8.51 min
β+
iron-53
H2CO3(aq)
or
carbonic acid
220Fr
27.4 s
α
francium-220
CO2(aq)
3H
12.31 y
β-
hydrogen-3
CH3COOH(aq)
ethanoic acid
131I
8.021 d
β-
iodine-131
or
(acetic acid)
HC2H3O2(aq)
37K
1.23 s
β+
potassium-37
42K
12.36 h
β-
potassium-42
85Kr
10.73 y
β-
krypton-85
Table L
Common Bases
16N
7.13 s
β-
nitrogen-16
19Ne
17.22 s
β+
neon-19
Formula
Name
32P
14.28 d
β-
phosphorus-32
NaOH(aq)
sodium hydroxide
239Pu
2.410 × 104 y
α
plutonium-239
KOH(aq)
potassium hydroxide
226Ra
1599 y
α
radium-226
Ca(OH)2(aq)
calcium hydroxide
222Rn
3.823 d
α
radon-222
NH3(aq)
aqueous ammonia
90Sr
29.1 y
β-
strontium-90
99
Tc
2.13 × 105 y
β-
technetium-99
Table M
232Th
1.40 × 1010 y
α
thorium-232
Common Acid-Base Indicators
233U
1.592 × 105 y
α
uranium-233
Approximate
235U
7.04 × 108 y
α
uranium-235
Indicator
pH Range
Color
for Color
Change
238U
4.47 × 109 y
α
uranium-238
Change
Source: CRC Handbook of Chemistry and Physics, 91st ed., 2010-2011,
CRC Press
methyl orange
3.1-4.4
red to yellow
bromthymol blue
6.0-7.6
yellow to blue
phenolphthalein
8-9
colorless to pink
litmus
4.5-8.3
red to blue
bromcresol green
3.8-5.4
yellow to blue
thymol blue
8.0-9.6
yellow to blue
Source: The Merck Index, 14th ed., 2006, Merck Publishing Group
Reference Tables for Physical Setting/Chemistry - 2011 Edition
6
Table O
Symbols Used in Nuclear Chemistry
Name
Notation
Symbol
4
alpha particle
α
2He or 2α
0
0
beta particle
or
β-
-1e
-1β
0
gamma radiation
γ
0γ
1
neutron
n
0n
1
proton
p
1H or 1p
0
0
positron
or
β+
+1e
+1β
Table P
Organic Prefixes
Prefix
Number of
Carbon Atoms
meth-
1
eth-
2
prop-
3
but-
4
pent-
5
hex-
6
hept-
7
oct-
8
non-
9
dec-
10
Table Q
Homologous Series of Hydrocarbons
General
Examples
Name
Formula
Name
Structural Formula
H
H
alkanes
CnH2n+2
ethane
H
C C
H
H H
H
H
alkenes
CnH2n
ethene
C C
H
H
alkynes
CnH2n-2
ethyne
H C C H
Note: n = number of carbon atoms
Reference Tables for Physical Setting/Chemistry - 2011 Edition
7
Table R
Organic Functional Groups
Class of
Functional
General
Example
Compound
Group
Formula
F (fluoro-)
R X
halide
Cl (chloro-)
(X represents
CH3CHClCH3
(halocarbon)
Br (bromo-)
any halogen)
2-chloropropane
I (iodo-)
CH3CH2CH2OH
alcohol
OH
R
OH
1-propanol
CH3OCH2CH3
ether
O
R
O R′
methyl ethyl ether
O
O
O
aldehyde
CH3CH2C H
C H
R
C H
propanal
O
O
O
ketone
CH3CCH2CH2CH3
C
R
C R′
2-pentanone
O
O
O
organic acid
CH3CH2C OH
C OH
R
C OH
propanoic acid
O
O
O
ester
CH3CH2COCH3
C O
R
C O R′
methyl propanoate
R′
CH3CH2CH2NH2
amine
N
R
N R′′
1-propanamine
O
O
O R′
amide
CH3CH2C NH2
C NH
R
C NH
propanamide
Note: R represents a bonded atom or group of atoms.
Reference Tables for Physical Setting/Chemistry - 2011 Edition
8
Reference Tables for Physical Setting/Chemistry - 2011 Edition
9
Reference Tables for Physical Setting/Chemistry - 2011 Edition
10
Reference Tables for Physical Setting/Chemistry - 2011 Edition
11
Table T
Important Formulas and Equations
d = density
m
Density
d =
m = mass
V
V = volume
given mass
Mole Calculations
number of moles =
gram-formula mass
measured value - accepted value
Percent Error
% error =
× 100
accepted value
mass of part
Percent Composition
% composition by mass =
× 100
mass of whole
mass of solute
parts per million =
× 1000000
mass of solution
Concentration
moles of solute
molarity =
liter of solution
P = pressure
P1V1
P2V2
Combined Gas Law
=
V = volume
T1
T2
T = temperature
MA = molarity of H+MB = molarity of OH-
Titration
MAVA = MBVB
VA = volume of acid
VB = volume of base
q = mCΔT
q = heat
Hf = heat of fusion
Heat
q = mHf
m = mass
Hv = heat of vaporization
q = mHv
C = specific heat capacity
ΔT = change in temperature
K = °C + 273
K = kelvin
Temperature
°C = degree Celsius
DET 609 ADU
Reference Tables for Physical Setting/Chemistry - 2011 Edition
12